Explanation of thermodynamic system, surrounding and boundary with best examples
Dear readers, You may understand easily about thermodynamic system, Surrounding and Boundary with explained examples. This article helps to understand these thermodynamic terms in easy way. Tell about this post in comment section.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Thermodynamic system
2. Types of thermodynamic systems
1.1 Open system
1.2 Closed system
1.3 Isolated system
3. Surroundings
4. Boundary
1. Thermodynamic system
- The thermodynamic system (simply known as system) may be defined as a definite area or a space where some thermodynamic process is taking place.
- It is a region where our attention is focussed for studying a thermodynamic process.
- A little observation will show that a thermodynamic system has its boundaries and anything outside the boundaries is called its surroundings as shown in fig.
- These boundaries may be fixed like that of a tank enclosing a certain mass of compressed gas, or movable like boundary of a certain volume of liquid in a pipe line.

1.1 Types
of thermodynamic systems

i.
Closed
system(Non flow process)
ii.
Open
system (Flow process)
iii.
Isolated system
i.
Closed system:
In
a closed system or non-flow system, Energy crosses the system boundary in the
form of heat and work, but there is no mass transfer.
Example:
Gas contained in the cylinder
Note the above picture. Yes! this is a closed vessel otherwise we can see as a cylinder. It is the storage device which stores any gas. Which is used in many areas like industries, home, hospitals etc., We can fill the gas in long time in closed condition. So there is no mass transfer. Now i am going to heat this cylinder. What will happen is, heat energy is transferred to gas through cylinder. If i further heat this cylinder that will be burst. That means heated gas gives some amount of work. So we can take it as a best example for closed system because there is a no mass transfer, there is a heat and work transfer.
ii. Open
system:
In
an open system or flow system or control volume system, both energy and mass
(heat and work) cross the boundary of the system
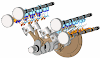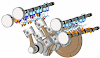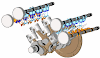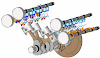
Examples: Engine, Air compressor and turbines
Engine is a best example for open system. Let see how, Engine is a device which converts heat energy into useful work in a cyclic process. It is used in a petrol and diesel vehicles. There is a mass transfer in a every cycle during intake and exhaust stroke. There is a heat transfer after the combustion process. There is a work transfer in piston and crank shaft. Connecting rod transfers the work to crank shaft from piston.
iii. Isolated system:
In an
isolated system no mass and no energy crosses the boundary of the system.
2. Surroundings
Everything outside of the system which affects the behaviour of the system is called surroundings.
3. Boundary
The system and surroundings are separated by the system boundary. It may be real or imaginary.










0 Comments
Write something...