1. Define Specific heat capacity of a gas.
It is defined as the amount of heat required to raise or lower the temperature of a unit mass of any substance through one degree. Its unit is kJ/kg K. It is denoted by ‘C’.
2. State the Avagadro’s law.
It states “Equal volume of all gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain equal number of molecules”.
Mathematically M. V = constant
3. Define Absolute temperature
Absolute zero temperature is taken as -273°C. The temperatures measured from this zero are called absolute temperatures. The absolute temperature in Celsius scale is called degree Kelvin (K). Mathematically,
Absolute Temperature in K = Temperature in °C + 273
4. State the types of thermodynamic systems.
There are various types of thermodynamic systems available some of them are,
- Constant volume process
- Constant pressure process
When a system undergoes a cyclic process, the algebraic sum of the work transfer is proportional to the algebraic sum of the heat transfer.
Mathematically, ∮𝛿Q = ∮𝛿W
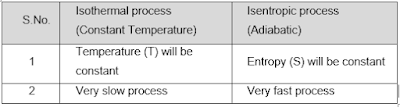
6. Write any 2 differences between isothermal and adiabatic process
7. Name the four processes of carnot cycle
Cornot cycle consists of two isothermal processes and Two Isentropic processes.
8. What is air standard efficiency?
The thermal efficiency of the engine which uses air as the working medium is known as ‘Air standard Efficiency’. This efficiency is often called as Ideal efficiency
Air standard efficiency (ɳ ) = Workdone/Heat Supplied.
9. Write any 2 assumptions made in deriving air standard efficiency
- The working medium or air in the engine cylinder is a perfect gas i.e. It obeys the gas laws and has constant specific heats
- The compression and the expansion process are adiabatic and they take place without internal friction
10. Draw p-V diagram of a diesel cycle
11. What is diesel knock?
If ignition delay is long, much larger quantity of the fuel has been injected before the first droplets burn and this may result in too high a rate of combustion, giving rise to very high rates of pressure rise and also higher peak pressures, causing a peculiar thudding sound known as diesel knock.
12. Write the combustion stages in 4 stroke SI engine
- Ignition delay
- Rapid combustion
- After burning
- Should have high calorific value
- Should produce less smoke
14. Define calorific value of fuel
It is defined as the amount of heat produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel.
15. What are the merits of solid fuel?
- They are easy to transport.
- They are convenient to store without any risk of spontaneous explosion.
- Their cost of production is low.
- They possess moderate ignition temperature.
If the heat contained in the water vapour could be recovered then it has high calorific value.
17. Define cetane number.
It is defined as the percentage volume of normal cetane in a mixture of normal cetane and alpha methyl naphthalene which gas the same tendency to knock as the fuel under examination.
18. What is Esterification?
Esterification is the general name for a chemical reaction in which two reactants (typically an alcohol and an acid with a catalyst) form an ester as the reaction product. Bio diesel is manufactured using this process.
19. What is brake power?
Net power developed by the engine at the output shaft is called as brake power.
It is measured by using dynamo meter
BP = 2πNT (kW) When Torque in kN, Speed in rps
20. Name the various methods of measuring brake power
- Prony brake dynamometer
- Eddy current brake dynamometer
- Rope brake dynamometer
It is defined as the ratio of indicated power to heat supplied to the engine.
22. Define indicated mean effective pressure
IMEP (Indicated mean effective pressure) is defined as the average pressure acting on a piston during the portions of one complete working cycle in an IC engine.
23. What is friction power?
It is defined as the difference between indicated power and brake power.
Unit of friction power is kW.
FP = IP – BP
24. Define mechanical efficiency
It is the ratio between brake power to indicated power.
25. What is COP?
COP of refrigeration is defined as “The ratio of refrigeration effect (QLoss) to the work input (WInput)”. It measures the effectiveness of refrigeration system.

26. Define wet bulb temperature
- The value indicated by a wet-bulb thermometer often provides an adequate approximation of the thermodynamic wet-bulb temperature.
- A psychrometer is a device that includes both a dry-bulb and a wet-bulb thermometer
27. State the desirable properties of the refrigerants
- Refrigerant should have low boiling point.
- It should have corrosive resistance.
28. Name the psychrometric properties
- Dry bulb temperature
- Wet bulb temperature
29. What is Refrigerating Effect?
It is defined as a output of the refrigeration.
Mathematically ∆h = m Cp dT = h1 – h4
30. What is humidification?
The process in which the moisture or water vapor or humidity is added to the air without changing its dry bulb (DB) temperature is called as humidification process.






0 Comments
Write something...