How does a bomb calorimeter works? How to find higher calorific value in bomb calorimeter
Procedure to measure calorific value of solid and liquid fuels in bomb calorimeter
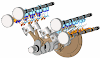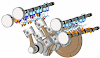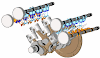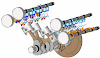
- The bomb calorimeter is used to determine the calorific values of solid and liquid fuels.
- It consists of a strong steel shell known as a bomb.
- It consists of a base which supports the platinum crucible and is screwed to the body of the bomb.
- The top of the bomb carries an oxygen supply connection and a valve to release the product.
- One gram of powdered sample coal is taken for the test and the calorimeter is filled with 2000cm3 of water.
- The sample is placed in the platinum crucible.
- The iron fuse wire which surrounds the sample of coal, is connected to the lower end of the two electrodes.
- The electrodes extend through the base of the bomb and connect the fuse wire to an electric circuit. The coal can be ignited by closing the electric circuit.
- The bomb is placed inside a copper vessel which contains water.
- There is a stirring device for agitating the water within the calorimeter.
- The calorimeter containing the bomb is placed in another container which acts as a heat insulator.
- The temperature of water in the calorimeter is measured by a thermometer.
- The oxygen cylinder is coupled to the bomb and oxygen is admitted to the bomb through the value until the pressure gauge in the cylinder indicates a pressure of 25 atmospheres.
- The fuel is ignited by passing a current through the fuse wire.
- The temperature of both starts increasing and the readings on the thermometer are taken at one minute intervals for 10 minutes, after the maximum intervals for 10 minutes, after the maximum temperature is reached.
- Thereafter the temperature starts falling slowly. When the temperature fall shows a steady rate the readings are taken at regular intervals for an additional five minutes.
- Heat given by the combustion of coal + Heat given by the combustion of fuse wire = Heat taken by the water and calorimeter.







0 Comments
Write something...